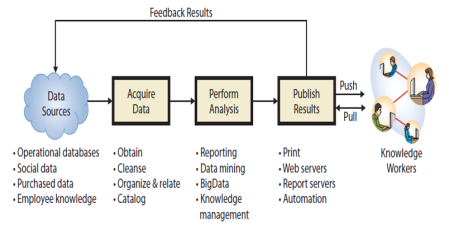
What Are the Functions and Organization of the IS Department?
- Plan how to use IS to accomplish organizational goals and strategy.
- Manage outsourcing relationships.
- Protect information assets.
- Develop, operate, and maintain organization's computing infrastructure.
- Develop, operate, and maintain enterprise applications.
How Is the IS Department Organized?
Chief Information Officer (CIO)-a common title for the principal manager of the IS department though it varies from organization.
- Other common titles: Vice President of Information Services, Director of Information Services, and less commonly, Director of Computer Services.
Chief Technology Officer (CTO)-often heads the technology group.
- Evaluates new technologies, new ideas, and new capabilities and identifies those that are most relevant to the organization.
- Job requires deep knowledge of information technology and the ability to envision and innovate applications for the organization.
Chief Security Officer (CSO)-manages security for all of the organization's assets: physical plant and equipment, employees, intellectual property, and digital. The CSO reports to the CEO.
Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)-manages security for the organization's information systems and information. The CISO reports to the CIO.
What IS-Related Job Positions Exist?
How Do Organizations Plan the Use of IS?
- Align information systems with organizational strategy; maintain alignment as organization changes.
- Communicate IS/IT issues to executive group.
- Develop/enforce IS priorities within the IS department.
- Sponsor steering committee.
- Steering committee-is a group of senior managers from the major business functions that works with the CIO to set the IS priorities and decide among major IS projects and alternatives.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing?
Outsourcing-is the process of hiring another organization to perform a service.
- Done to save costs, to gain expertise, and to free management time.
Popular Reasons for Outsourcing IS Services
IS/IT Outsourcing Alternatives
Outsourcing Risks
What Are Your User Rights and Responsibilities?
User Information Systems Rights and Responsibilities
2026?
- Most organizations will move their internal hardware infrastructure into the cloud.
- Rise of mobile devices at work.
- Cheaper, more powerful, with dynamic, maybe even gamelike user experiences.
- Organizations develop BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies that meet their needs and strategies, and many will encourage employees to bring their own devices to work.
- IoT (the Internet of Things) will offer the opportunity for innovation in operations, manufacturing, and supply chain management.
- Organizations will use social media inside the organization in true Enterprise 2.0 style.
- Organizational culture